Topic 17 Shiny Dashboard and Storyboard
We have two package options for building Shiny dashboards: flexdashboard and shinydashboard.
17.1 flexdashboard
Easy interactive dashboards for R that use R Markdown to publish a group of related data visualizations as a dashboard, support a wide variety of components including
htmlwidgets- A framework for embedding JavaScript visualizations into R;base,lattice, andgridgraphics;tabular data;gaugesandvalue boxes;text annotations.
A flexdashboard is flexible and easy to specify row and column-based layouts with re-sizing to fill the browser. `It is just a document that looks like a dashboard. However, it
contains some specific widgets designed to work in a dashboard layout.
offers storyboard layouts for presenting sequences of visualizations and related commentary
can use Shiny to drive visualizations dynamically by specifying
runtime: shinyin the YAML head.can only run interactive code client-side (in embedded JavaScript).
17.2 shinydashboard
An R package for creating dashboard-style layouts with Shiny that uses
Bootstrap (a free open source front-end-framework develops faster, easier, responsive web pages) for layout;
uses AdminLTE, which is a theme built on top of Bootstrap.
Unlike flexdashboard, shinydashboard has three structured components:
## app.R ##
library(shiny)
library(shinydashboard)
ui <- dashboardPage(
dashboardHeader(),
dashboardSidebar(),
dashboardBody()
)
server <- function(input, output) { }
shinyApp(ui, server)shinydashboard needs a server behind it to execute R code on user input. It can implement a dashboard layout that contains some specific widgets designed to work in a dashboard layout. It can also run interactive code either by processing server-side (in R) or client-side (in embedded JavaScript).
17.3 Three Web Application Terms
Responsive: adapting layouts to a variety of screen and window sizes.
Interactive: elements that react to your actions on the site.
Reactive: automatically checking and updating data from the server without refreshing the website.
17.4 Using Flexdashboard
This note outlines the flexdashboard using Shiny.
17.4.1 Components
We can use flexdashboard to publish groups of related data visualizations as a dashboard. A flexdashboard can either be static (a standard web page) or dynamic (a Shiny interactive document). A wide variety of components can be included in flexdashboard layouts, including:
Interactive data visualizations based on htmlwidgets.
R graphical output including base, lattice, and grid graphics.
Tabular data (with optional sorting, filtering, and paging).
Value boxes for highlighting important summary data.
Gauges for displaying values on a meter within a specified range.
Text annotations of various kinds.
17.4.2 Basic Flexdashboar Layout
The layout design is relatively simpler than that of shinydashboard.
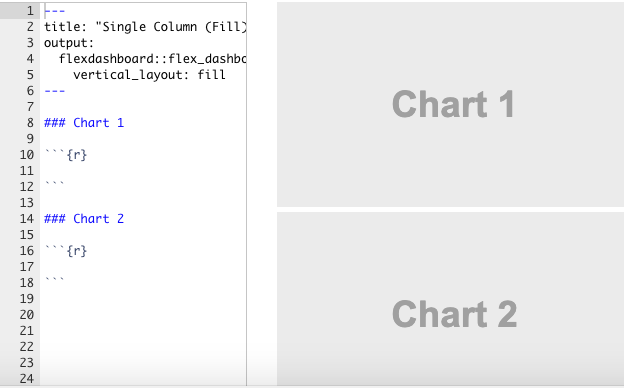
17.4.2.1 Single Column
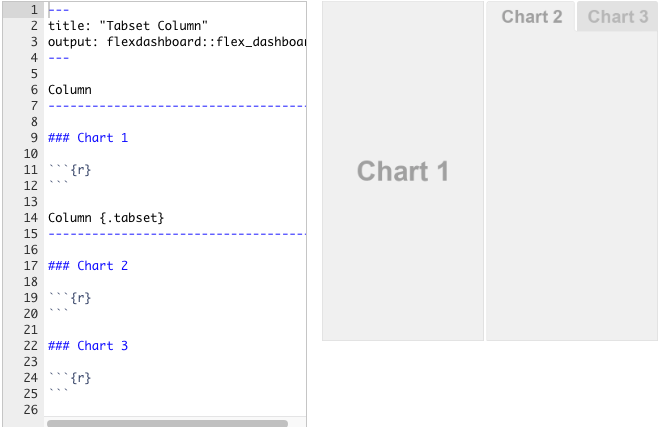
Flexdashboards are divided into columns and rows, with output components delineated using level 3 markdown headers (###). By default, dashboards are laid out within a single column, with charts stacked vertically within a column and sized to fill available browser height.
17.4.2.2 Multiple Column
To layout charts using multiple columns, we introduce a level 2 markdown header (--------------) for each column.

17.4.2.3 Row Orientation
We can also choose to orient dashboards row-wise rather than column-wise by specifying the orientation: rows option.

17.5 Storyboards
Storyboards are an alternative to the row and column-based layout schemes described above that are well suited to presenting a sequence of data visualizations and related commentary.
17.5.1 Storyboard Basics
To create a storyboard layout you do the following:
Add the storyboard: true option to the dashboard.
Include a set of
level 3 (###)dashboard components. Each component will be allocated its own frame in the storyboard, with the section title used as the navigation caption.
The basics of creating storyboards are explained below. For a more complete example, see the HTML Widgets Showcase storyboard.